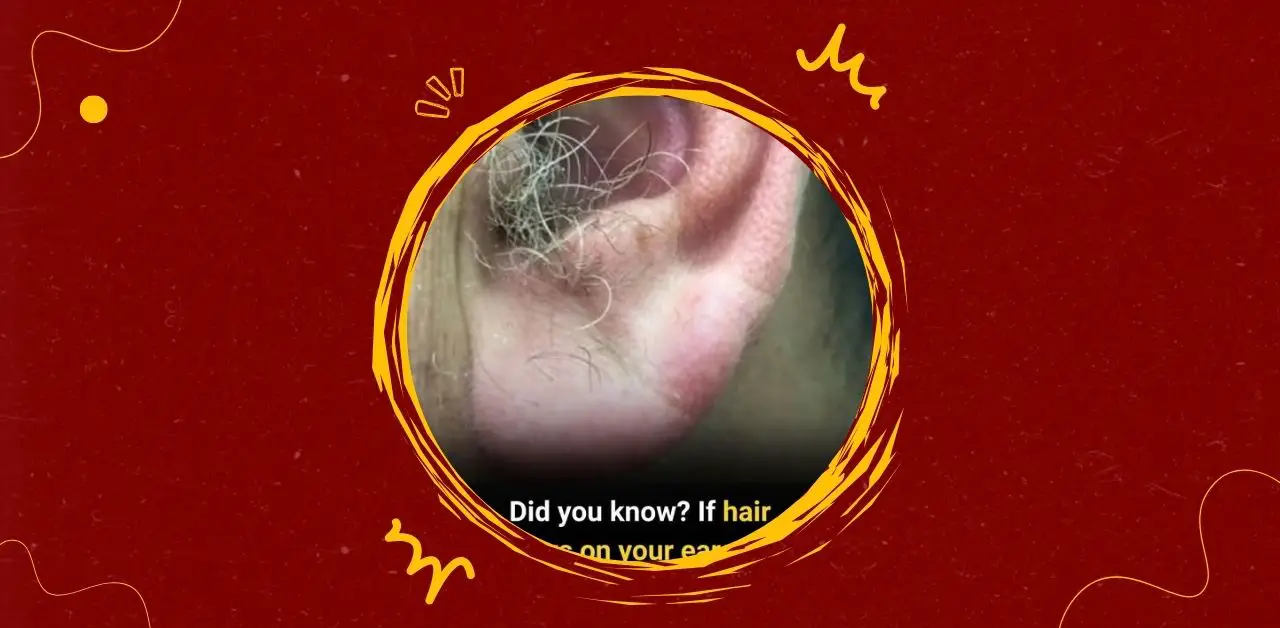
Ear hair, medically referred to as auricular hypertrichosis, is the presence of noticeable hair on or around the outer ear. While it doesn’t affect hearing, it often raises curiosity and sometimes self-consciousness. Many people begin to notice ear hair as they age, particularly men, and wonder what it means for their health. Understanding why it happens and how to manage it can help normalize this natural change.
Why Ear Hair Appears
- Hormonal Influence: Ear hair growth is strongly linked to androgen hormones, especially testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Over time, hair follicles in certain areas become more sensitive to these hormones, leading to thicker, coarser growth.
- Genetics: Family history plays a role. Some individuals are genetically predisposed to develop more visible ear hair.
- Aging: As people grow older, hair growth patterns shift. Follicles that once produced fine, nearly invisible hair may start producing darker, more noticeable strands.
Is Ear Hair Harmful?
- Normal Variation: Ear hair is generally harmless and considered a normal part of aging.
- No Impact on Hearing: It doesn’t interfere with auditory function.
- Cosmetic Concern: The main issue is aesthetic. Some people feel self-conscious about visible ear hair, especially if it grows long or thick.
Myths and Misconceptions
- Heart Disease Connection: Older studies suggested a link between ear hair and heart disease, but modern research does not support this as a reliable indicator.
- Sign of Poor Health: Ear hair is not a symptom of illness. It’s primarily a result of hormonal and genetic factors.
Managing Ear Hair
- Trimming: Small grooming scissors or electric trimmers can safely shorten ear hair.
- Waxing or Plucking: These methods remove hair from the root but may cause discomfort or irritation.
- Laser Hair Removal: A longer-term solution that reduces regrowth by targeting follicles.
- Professional Care: Dermatologists or trained aestheticians can provide safe removal options.
Practical Considerations
- Safety First: Avoid inserting sharp tools deep into the ear canal. Focus only on visible outer ear hair.
- Consistency: Hair will regrow, so regular maintenance is needed if removal is desired.
- Personal Choice: Some embrace ear hair as a natural part of aging, while others prefer grooming. Both approaches are valid.
Conclusion
Ear hair growth is a natural, common occurrence influenced by hormones, genetics, and age. While it may spark curiosity or cosmetic concern, it poses no health risks and doesn’t affect hearing. Managing it is a matter of personal preference, with safe options ranging from simple trimming to professional treatments. Rather than viewing ear hair as a problem, it can be understood as another sign of the body’s evolving relationship with age and hormones.